In
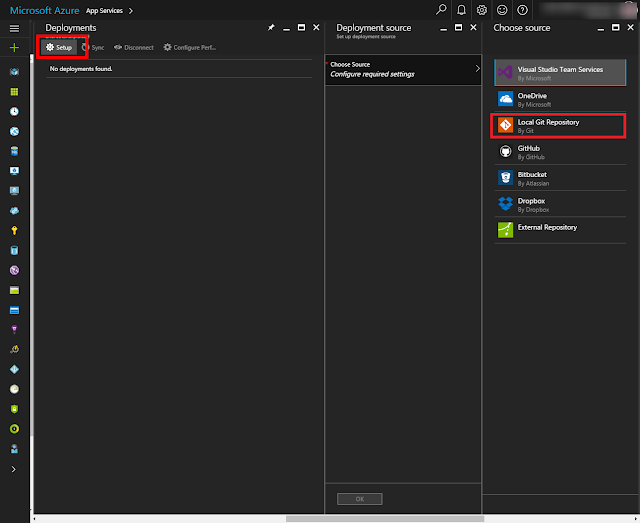
Part 1, you already knew how to create an Azure Chat Bot and deploy it from a local repository. In this article, I'll show you how to apply a Luis app into the bot and how to integrate it with Facebook Messenger.
1. Go to
luis.ai website and create an app.
This Luis app will be used for a Pizza shop, so we create 3 intents:
greeting,
pizza and
noservice. We also create an simple entity named
topping:
And below are utterances for intents:
Here are another samples of utterances for
pizza intent (you should map label topping every time inputting):
can i have pizza with pineapple and bacon
i would like a pizza with cheese bacon and pineapple
may i have pizza with pineapple and sausage
can i get tomato with cheese on my pizza
my pizza should have goat cheese and mozzarella on it
You can add more utterances. After inputting data, click Train & Test link and click Train Application button. Then keying sentences into Interactive Testing box:
If the training & test are ok, let publish the app:
2. Congratulation! You already had first Luis app, let link it with your bot service on Azure. Open the bot on Azure, click on
SETTINGS tab and select the Luis app then click
Save changes button:
Now, we will enhance the bot with power from the Luis app. Below is the code of the bot, it will recognize intents & entities from chat message to make corresponding response:
"use strict";
var builder = require("botbuilder");
var botbuilder_azure = require("botbuilder-azure");
var useEmulator = (process.env.NODE_ENV == 'development');
var connector = useEmulator ? new builder.ChatConnector() : new botbuilder_azure.BotServiceConnector({
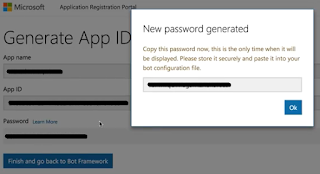
appId: process.env['MicrosoftAppId'],
appPassword: process.env['MicrosoftAppPassword'],
stateEndpoint: process.env['BotStateEndpoint'],
openIdMetadata: process.env['BotOpenIdMetadata']
});
var bot = new builder.UniversalBot(connector);
var luisAppId = process.env.LuisAppId;
var luisAPIKey = process.env.LuisAPIKey;
var luisAPIHostName = process.env.LuisAPIHostName || 'api.projectoxford.ai';
const LuisModelUrl = 'https://' + luisAPIHostName + '/luis/v2.0/apps/' + luisAppId + '?subscription-key=' + luisAPIKey + '&verbose=true';
var recognizer = new builder.LuisRecognizer(LuisModelUrl);
var intents = new builder.IntentDialog({ recognizers: [recognizer] })
.matches('None', (session, args) => {
session.send('Hello, welcome to Pizza Shop. How may I help you?');
})
.matches('greeting', (session, args) => {
session.send('Hello, welcome to Pizza Shop. How may I help you?');
})
.matches('pizza', (session, args) => {
var topping = builder.EntityRecognizer.findEntity(args.entities, 'topping');
if(topping) session.send('Thank you for ordering. Your pizza with %s will be delivered to you in 30 minutes.', topping.entity);
else session.send('Thank you for ordering. Would you like your pizza with anything else?');
})
.matches('noservice', (session, args) => {
session.send('Thank you for ordering but we only sell pizza. Comeback later if you want a pizza.');
})
.onDefault((session, args) => {
session.send('Sorry! I am a support bot, I did not understand \'%s\'. Please call XXXXX, our staff will be happy to help you.', session.message.text);
});
bot.dialog('/', intents);
if (useEmulator) {
var restify = require('restify');
var server = restify.createServer();
server.listen(3978, function() {
console.log('test bot endpont at http://localhost:3978/api/messages');
});
server.post('/api/messages', connector.listen());
} else {
module.exports = { default: connector.listen() }
}
Ok, let see our bot working:
3. We now have a bot serving our Pizza Shop, let connect it with Facebook so our customers can order pizza via Facebook messenger :)
To do that, you must have a Facebook Page and a Facebook Application. In the case of you don't have your Facebook Page, you can read
this article for how to. If you don't have any Facebook Application, you can
read here to register one.
Assuming that you already had your Facebook Application, go to link
https://developers.facebook.com and open the application. Below is mine for example:
(Picture 1)
In the above picture, I already added Messenger product into my app. If you don't add yet, click
+ Add Product link >> find
Messenger product then click
Get Started button to add (see the following picture).
After that, go to
https://dev.botframework.com/bots, open your bot on MS Bot Framework, find
Facebook Messenger in
Add a channel section then click to add and configure it. Scroll down to
Callback URL and Verify Token for Facebook and copy values of
Callback URL and
Verify Token. They will be used for configuring
Webhooks on your Facebook Application.
(Picture 2)
Back to the
Facebook Application, click
Setup Webhooks button to verify the callback URL of your bot:
(Picture 3)
Provide values copied from your bot (
Picture 2) in to the opened box, select
Subscription Fields (events) you want:
And click
Verify and Save button. When done, let select your
Facebook Page and click
Subscribe button to subscribe the webhook to the page events:
To enable your app to send and receive messages using your
Facebook Page for everyone coming to your page (public), you must add
pages_messaging and submit to review (see this link
https://developers.facebook.com/docs/messenger-platform/app-review for more info on this process) :
Otherwise you must add
Developers or
Testers for testing. You can do via
Roles function:
Yeah! You finished necessary steps on Facebook. Return to the configuration of Facebook Messenger on your bot, let key values from Facebook into:
Facebook Page ID: find on the
About menu of your Facebook Page:
Facebook App ID & App Secret: get from the dashboard of your Facebook App (
Picture 1).
Page Access Token: get from
Picture 3 when you select your page.
After keying above values, click Save button, your bot now is connected with Facebook Messenger:
It's time for talking with your bot. You can try via
https://www.messenger.com/t/<Your Page ID> or use Facebook Messenger on your mobile:
Those are basic steps for creating your bot with MS Bot Framework and connect it with channels like Facebook Messenger. I hope you have a quick start for your bot.
Good luck! Any comment is welcome.