- Server: an enhancement of previous server in Build JWT authentication server with Node.js, Express and MySQL by adding new todos API allowing to get, create new and delete todos based on user role authentication. You can clone / download the source code of this server on my GitHub: https://github.com/vnheros/nodejs-mysql-jwt-auth
- App: a todo app which allows user login or sign up new account. After login successfully, it will displays a list of public todos or todos of user. User can add new todo or delete an existing todo. You can clone / download the source code of this server on my GitHub (tested with Ionic 2 RC1): https://github.com/vnheros/ionic2-todos-example
1. My SQL DB
There are 2 tables: users and todos having script as below:
CREATE TABLE `users` (
`id` int(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`username` varchar(20) NOT NULL,
`password` varchar(20) NOT NULL,
`email` varchar(50) NOT NULL,
`role` varchar(20) DEFAULT 'Regitered',
PRIMARY KEY (`id`,`username`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT=6 DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;
CREATE TABLE `todos` (
`id` int(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`task` varchar(150) NOT NULL,
`deadline` timestamp NOT NULL DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP ON UPDATE CURRENT_TIMESTAMP,
`public` tinyint(1) NOT NULL DEFAULT '0',
`completed` tinyint(1) DEFAULT '0',
`username` varchar(20) DEFAULT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`id`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT=8 DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;
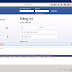
2. Design of todos app
Below are screens of this app:
3. Step to generate source code for the app
For Ionic 2 RC1, you should install its app-script to avoid some issues when running the app (read this post for more info).
Install @ionic/app-scripts and update your ionic 2:
#npm install @ionic/app-scripts@latest --save-dev
#npm install -g ionic
Generate providers then replace by the source code from my GitHub:
#ionic g provider Auth
#ionic g provider Todos
Generate pages then replace by the source code from my GitHub:
#ionic g page Welcome
#ionic g page Login
#ionic g page Signup
#ionic g page NewTodo
Add folder helpers then add file jwt-helper.ts (used to parse JWT in the app), add folder validators and add file password.ts (used to validate a password input when signing up). You can copy them from my GitHub.
From Ionic RCx, you will need to add pages and providers into app/app.module.ts to use them in your app. See my file on GitHub for example.
There are some another things in the source code which you can discover easily in the source code.
That's for to day and wish you have fun Halloween. Remember turn on the light.
Any comment is welcome.